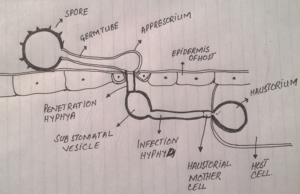
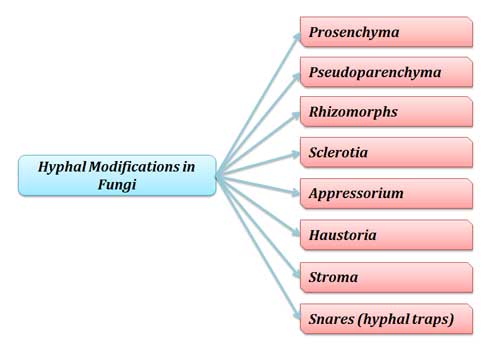
(1)Plectonchyma. A false tissue is formed by aggregation of hyphae. (A)Prisonchyma. It is loosely worn tissue of hyphae. They do not loose their identity. (B) Psedo phyrenchyma. Hyphae become woven and inter wind into a compact mass. They loose their identity. (2)Rhizomorphs. A thick strand or root like aggregation is called Rhizo morph. In rhizo morph hyphae loose their identity and whole mass behaves as organized unit. In Rhizo morph have higher injection capacity e.g armellarelia , melea. (3)Sclerotium. It is formed by aggretion and adhesion of hypae.Survive for longer period ( many year ) so these are called resting stage of fungi.Under favourable condition they are germinate and produce hypae and reproductive structure or spore. e.g clavicep purpure a Rhizocina solanine. Macroaphomina phenolics. (4)Stroma Any fungal tissue that forms reproductive structures is called stomata.Compact structures like matter. Generally sclerotia on germination form stroma. (5) Appresorium. These are common present in parasitic fungi ectoparasites. “An appresorium is simple terminal lobbed like structure of germinate is called appresorium”. It is adheres to surface of host and help to penetrate hyphae of pathogen into host tissues.e.g order erysiphales. (6) Haustorum. These are produced intra cellular mostly but usually intercellular . They secrete certain enzyme and hydrolyzes protein sccto and absorb nutrients from host with out. Houstonia also provide greater surface area for exchange of material.
.